Publications
You can find here my main journal and conference publications. Visit my Google Scholar profile for a full list of publications.
2024
- AEI
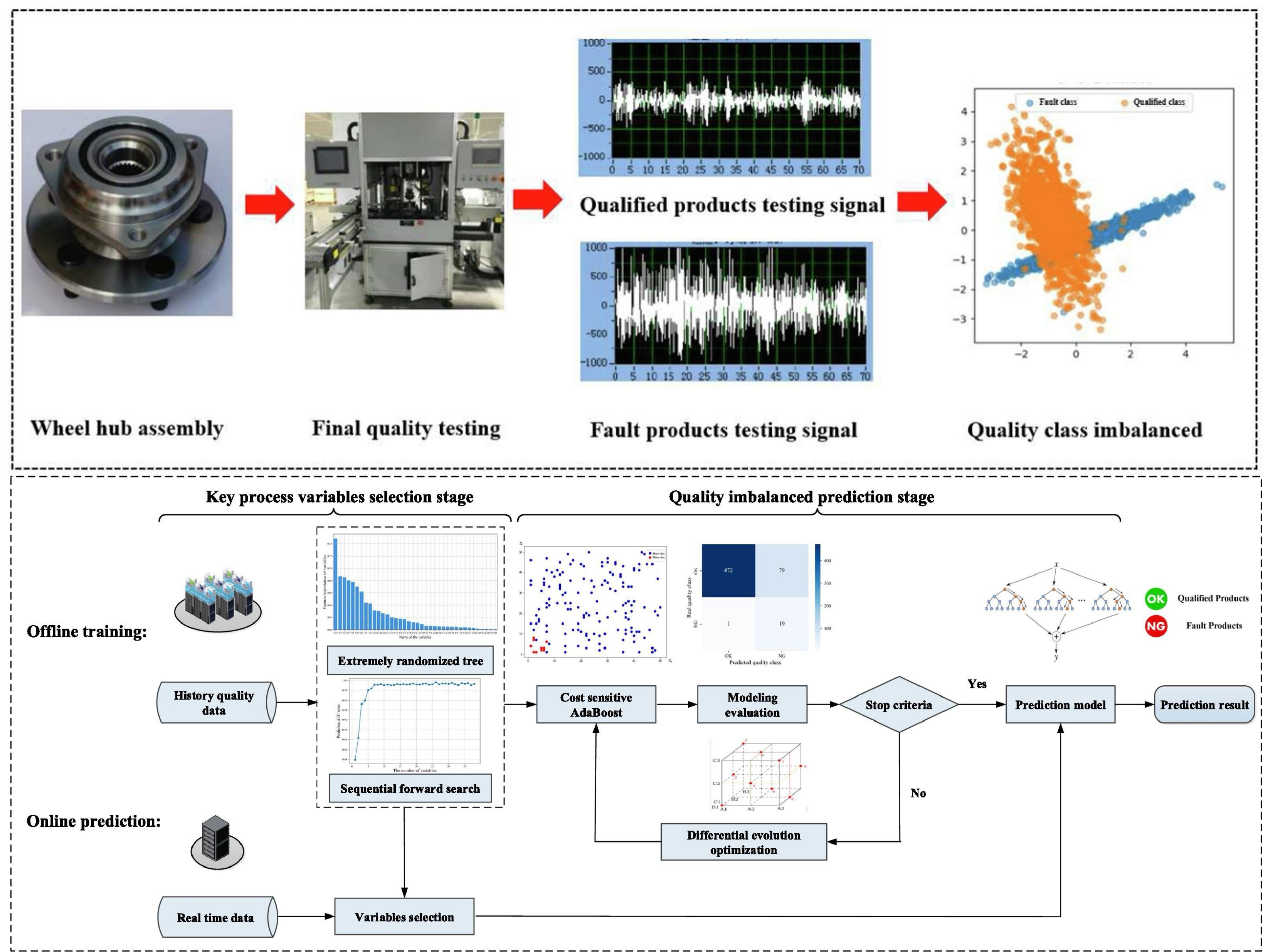 Two-stage imbalanced learning-based quality prediction method for wheel hub assemblyTianyue Wang, Tao Peng, Bingtao Hu, Ruirui Zhong, and 3 more authorsAdvanced Engineering Informatics, 2024
Two-stage imbalanced learning-based quality prediction method for wheel hub assemblyTianyue Wang, Tao Peng, Bingtao Hu, Ruirui Zhong, and 3 more authorsAdvanced Engineering Informatics, 2024To efficiently solve the problem of two-dimensional irregular polygon packing in actual production,a heuristic algorithm driven by design knowledge was proposed.No Fit Polygon (NFP) was used to judge the relative positions between irregular polygons,and a mathematical model of local fitness was established to measure the fitting degree of irregular polygons.Then,a mathematical model driven by design knowledge was established to evaluate the position of irregular polygons to be placed.A greedy algorithm based on local search strategy was used to complete the packing.The experimental testing of international common benchmark cases and comparison with existing intelligent optimization algorithms proved that the proposed algorithm had certain advantages in layout quality and time performance with high stability.Besides,the experimental test of the sample data in actual production proved that the proposed algorithm had the value of being applied to actual production applications.
@article{WANG2024102309, title = {Two-stage imbalanced learning-based quality prediction method for wheel hub assembly}, journal = {Advanced Engineering Informatics}, volume = {59}, pages = {102309}, year = {2024}, issn = {1474-0346}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2023.102309}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1474034623004378}, author = {Wang, Tianyue and Peng, Tao and Hu, Bingtao and Zhong, Ruirui and Feng, Yixiong and Chen, Xiangjun and Tan, Jianrong}, keywords = {Smart manufacturing, Quality prediction, Assembly production, Imbalanced data}, google_scholar_id = {UeHWp8X0CEIC} } - JED
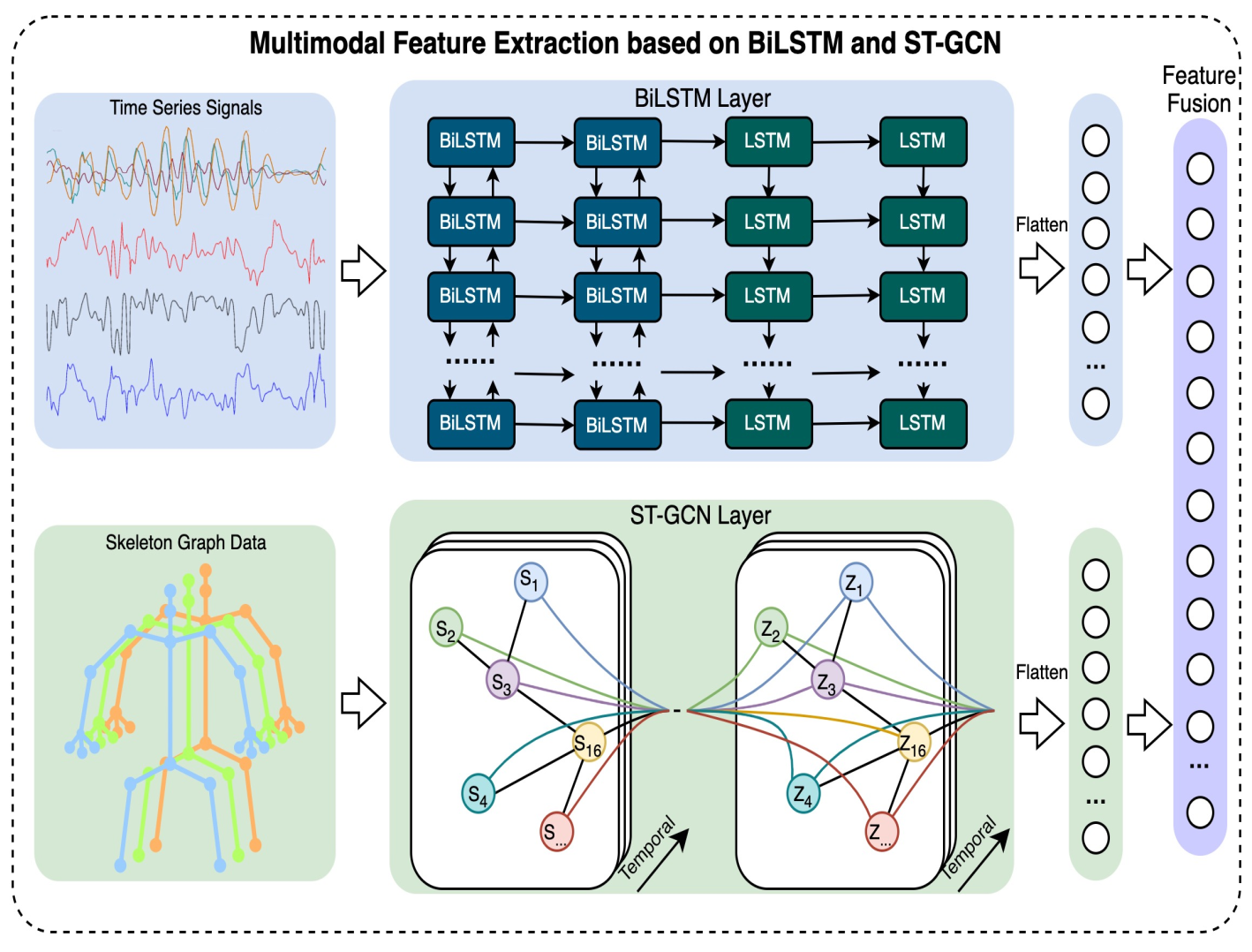 Human-Robot handover task intention recognition framework by fusing human digital twin and deep domain adaptationRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Zhaoxi Hong, Zhifeng Zhang, and 4 more authorsJournal of Engineering Design, 2024
Human-Robot handover task intention recognition framework by fusing human digital twin and deep domain adaptationRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Zhaoxi Hong, Zhifeng Zhang, and 4 more authorsJournal of Engineering Design, 2024Industry 5.0 is conceived to achieve the expected high level of smart manufacturing and the more proactive and adaptive human-robot collaboration (HRC). In particular, human-robot handover tasks (HRHTs) are a notably crucial aspect of HRC, and resolving how to motivate robots to comprehend human handover intentions constitutes an exigent issue that demands resolution. To address these problems, A framework that integrates hierarchical human digital twin (HHDT) and deep domain adaptation is proposed, where HHDT model is built to digitise the human physical and physiological state and enhance the robot’s perception of humans, a feature extractor-based on bidirectional long-short-term memory and spatio-temporal graph convolution network (BiLSTM-ST-GCN) is devised to extract latent spatio-temporal features of HRHTs intentions. Additionally, the framework incorporates a deep domain adaptation layer (DDAL) that facilitates knowledge transfer of HRHTs intentions by accounting for the distribution differences between the source and target operator objects. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed framework for HRHTs intention recognition and extraction of domain invariant features.
@article{zhong2024human, title = {Human-Robot handover task intention recognition framework by fusing human digital twin and deep domain adaptation}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Hong, Zhaoxi and Zhang, Zhifeng and Lou, Shanhe and Song, Xiuju and Feng, Yixiong and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Journal of Engineering Design}, pages = {1--17}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Taylor \& Francis}, google_scholar_id = {3fE2CSJIrl8C} } - 3E
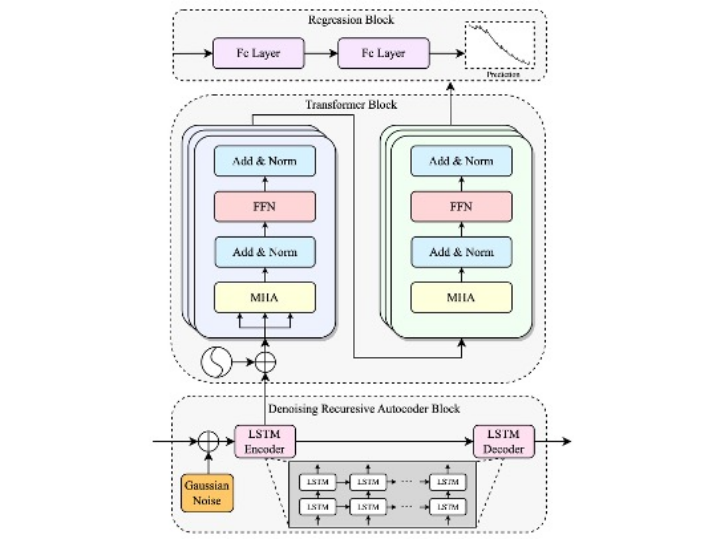 Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction: a federated learning-based approachRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Shanhe Lou, and 4 more authorsEnergy, Ecology and Environment, 2024
Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction: a federated learning-based approachRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Shanhe Lou, and 4 more authorsEnergy, Ecology and Environment, 2024In line with Industry 5.0 principles, energy systems form a vital part of sustainable smart manufacturing systems. As an integral component of energy systems, the importance of Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) batteries cannot be overstated. Accurately predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of these batteries is a paramount undertaking, as it impacts the overall reliability and sustainably of the smart manufacturing systems. Despite various existing methods have achieved good results, their applicability is limited due to the data isolation and data silos. To address the aforementioned challenges, this paper presents a novel federated learning (FL)-based approach that predicts the RUL of Li-ion batteries, thereby contributing to the sustainability of smart manufacturing. Firstly, a denoising recursive autoencoder-based transformer (DRAT) model is devised, focusing on extracting robust and latent features for RUL prediction under various conditions. Secondly, we propose an adaptive DRAT-based federated RUL framework (Fed-DRAT) for the collaborative modeling of Li-ion batteries RUL prediction for different energy systems. Specifically, an innovative adaptive model aggregation strategy is developed to equalize the contribution weights of different participating systems and improve model performance. Our extensive experiments with Li-ion batteries datasets indicate that our proposed DRAT significantly outperforms existing methods and demonstrates superior performance in different scenarios.
@article{zhong2024lithium, title = {Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction: a federated learning-based approach}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Feng, Yixiong and Lou, Shanhe and Hong, Zhaoxi and Wang, Fei and Li, Guangshen and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Energy, Ecology and Environment}, pages = {1--14}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, google_scholar_id = {Wp0gIr-vW9MC} } - FMSJ
 Smart scheduling of hanging workshop via digital twin and deep reinforcement learningJianguo Pan, Ruirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, and 2 more authorsFlexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 2024
Smart scheduling of hanging workshop via digital twin and deep reinforcement learningJianguo Pan, Ruirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, and 2 more authorsFlexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 2024The complexity of job-shop environments poses significant challenges for effective scheduling in the manufacturing industry. Flexible job-shop scheduling, in particular, involves coordinating multiple jobs with varying requirements across multiple machines, while considering various constraints and objectives. Traditional scheduling approaches often struggle to handle the dynamic nature inherent in such environments. To address the above challenges, this paper presents a digital twin (DT)-based management framework for hanging workshops, aiming to enhance flexible job-shop scheduling in manufacturing environments. The framework integrates real-time monitoring, condition monitoring, and smart scheduling capabilities to improve overall performance and efficiency. To implement the framework, a smart scheduling methodology based on a graph neural network and deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is devised. Markov Decision Process (MDP) captures the dynamic nature and uncertainties of the hanging workshop, while the graph embedding network technique represents operations, machines, and their relationships in a low-dimensional space. Decision-making is enhanced through training with the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm. Extensive Experiments are conducted to evaluate the framework’s effectiveness. The findings demonstrate the ability of the framework to improve job-shop scheduling performance.
@article{pan2024smart, title = {Smart scheduling of hanging workshop via digital twin and deep reinforcement learning}, author = {Pan, Jianguo and Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Feng, Yixiong and Zhang, Zhifeng and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal}, pages = {1--22}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, google_scholar_id = {dhFuZR0502QC} } - IET-CIM
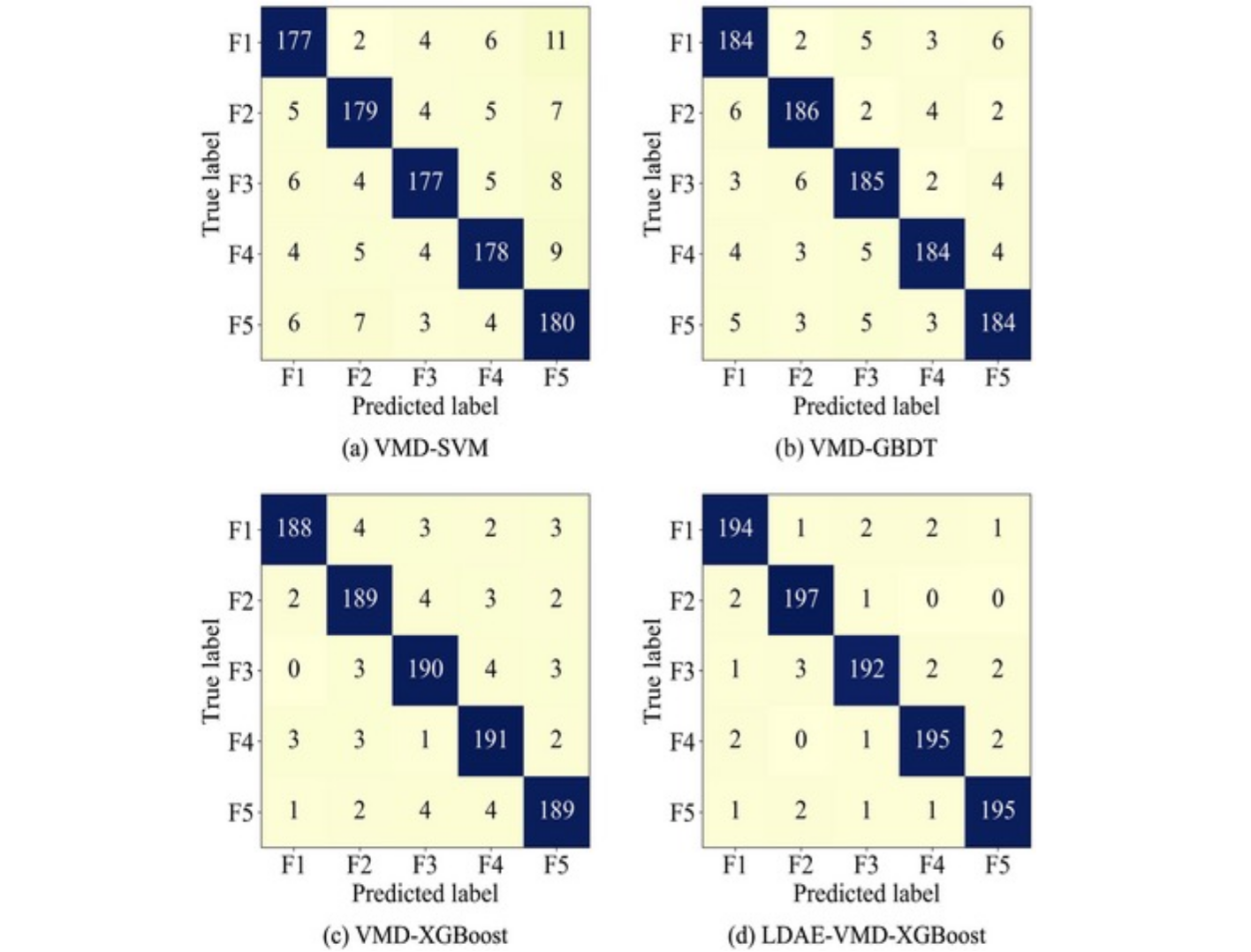 Uncertainty-aware Nuclear Power Turbine Vibration Fault Diagnosis Method Integrating Machine Learning and Heuristic AlgorithmRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Puyan Li, Xuanyu Wu, and 3 more authorsIET Collaborative Intelligent Manufacturing, 2024
Uncertainty-aware Nuclear Power Turbine Vibration Fault Diagnosis Method Integrating Machine Learning and Heuristic AlgorithmRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Puyan Li, Xuanyu Wu, and 3 more authorsIET Collaborative Intelligent Manufacturing, 2024Nuclear power turbine fault diagnosis is an important issue in the field of nuclear power safety. The numerous state parameters in the operation and maintenance of nuclear power turbines are collected, forming a complex high-dimensional feature space. These high-dimensional feature spaces contain redundant information, which increases the training cost and reduces the recognition accuracy and efficiency of the fault diagnosis model. To address the aforementioned challenges, a vibration fault diagnosis algorithm in nuclear power turbines is proposed. First, a long short-term memory-based denoising autoencoder (LDAE) is designed to enhance the capability of uncertainty awareness. Then, a feature extraction method integrating variational mode decomposition (VMD), L-cliffs-based effective mode selection, and sample entropy is devised to extract the latent features from the complex high-dimensional feature space. Furthermore, using extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) as the classifier, LDAE-VMD-XGBoost model is constructed for fault diagnosis of nuclear power turbines. Considering the impact of multiple hyperparameters of LDAE-VMD-XGBoost model on the performance, the pathfinder algorithm is used to optimise the model hyperparameter settings and improve the fault diagnosis accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate the performance of the proposed improved LDAE-VMD-XGBoost in accurate nuclear power turbine vibration fault diagnosis.
@article{zhong2024uncertain, title = {Uncertainty-aware Nuclear Power Turbine Vibration Fault Diagnosis Method Integrating Machine Learning and Heuristic Algorithm}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Feng, Yixiong and Li, Puyan and Wu, Xuanyu and Guo, Ao and Zhang, Ansi and Li, Chuanjiang}, journal = {IET Collaborative Intelligent Manufacturing}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Wiley}, google_scholar_id = {IWHjjKOFINEC} } - CASE 2024
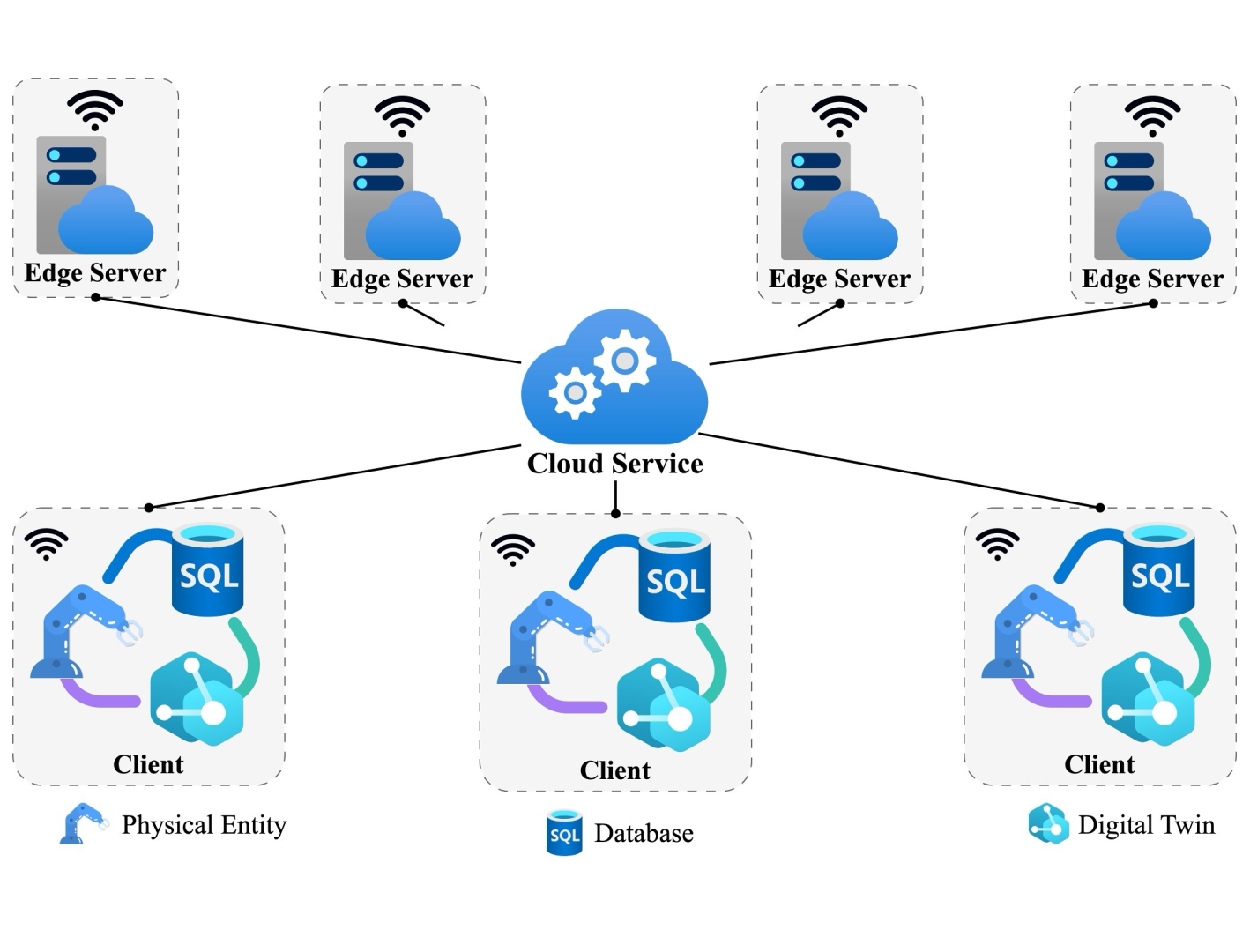 Edge Computing Empowered Digital Twin: An End-to-End Computing Task Scheduling ApproachRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Xiuju Song, Bingtao Hu, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE 20th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE) , 2024
Edge Computing Empowered Digital Twin: An End-to-End Computing Task Scheduling ApproachRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Xiuju Song, Bingtao Hu, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE 20th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE) , 2024The emerging of Digital Twin (DT) technology facilitates the further development of industrial automation. However, real-time and accurate DTs modeling and updating require massive communication and computing resources, which poses a challenge to limited resources. Edge computing as a distributed computing architecture offers the possibility of high-efficient resource scheduling in DTs. Motivated by this gap, this paper aim to solve the problem of real-time and high fidelity DTs modeling and updating. First, we represent the computing tasks of DTs in the form of Heterogeneous Computing Task Graph (HCTG). Then, a Hierarchical Attention Mechanism (HAT) is proposed to obtain the latent representation vectors of the HCTG. Finally, we design Markov Decision Process (MDP), and propose Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)-based computing task scheduling approach (HAT-DRL) to satisfy the minimum total completion time requirement of different DTs. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has promising scheduling performance and outperforms other task scheduling algorithms.
@inproceedings{zhong2024edge, title = {Edge Computing Empowered Digital Twin: An End-to-End Computing Task Scheduling Approach}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Feng, Yixiong and Song, Xiuju and Hu, Bingtao and Wang, Yong and Li, Puyan and Tan, Jianrong}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE 20th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE)}, pages = {3547--3552}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, google_scholar_id = {e5wmG9Sq2KIC} } - AEI
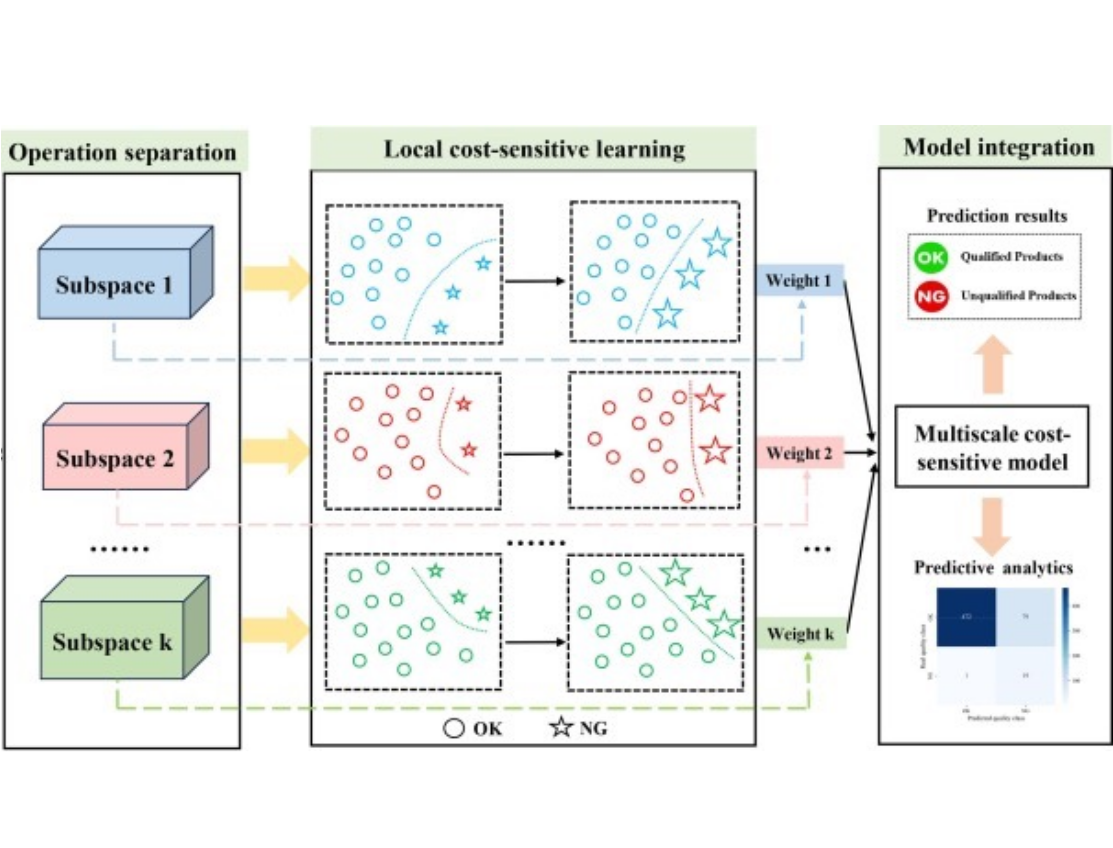 Multiscale cost-sensitive learning-based assembly quality prediction approach under imbalanced dataTianyue Wang, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Hao Gong, and 3 more authorsAdvanced Engineering Informatics, 2024
Multiscale cost-sensitive learning-based assembly quality prediction approach under imbalanced dataTianyue Wang, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Hao Gong, and 3 more authorsAdvanced Engineering Informatics, 2024Assembly quality prediction of complex products is vital in modern smart manufacturing systems. In recent years, data-driven approaches have obtained various outstanding engineering achievements in quality prediction. However, the imbalanced quality label makes it difficult for conventional quality prediction methods to learn accurate decision boundaries, resulting in weak prediction capabilities. Moreover, the multiple working condition data information in the assembly system presents another challenge to quality prediction. To handle the above issues, a multiscale cost-sensitive learning-based assembly quality prediction approach is proposed in this paper. First, an improved Gaussian mixture model is developed to automatically partition the global multi-condition data into several diverse subspaces. Then, the local cost-sensitive learning models are employed to tackle imbalanced data in each subspace. Finally, by leveraging Bayesian inference, multiple local cost-sensitive learning models are integrated to obtain a global multiscale prediction model. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, the quality prediction comparative experiments are conducted on two real-world assembly systems. The favorable results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in assembly quality prediction.
@article{wang2024multiscale, title = {Multiscale cost-sensitive learning-based assembly quality prediction approach under imbalanced data}, author = {Wang, Tianyue and Hu, Bingtao and Feng, Yixiong and Gong, Hao and Zhong, Ruirui and Yang, Chen and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Advanced Engineering Informatics}, volume = {62}, pages = {102860}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Elsevier}, google_scholar_id = {TQgYirikUcIC} } - ICNSC 2024
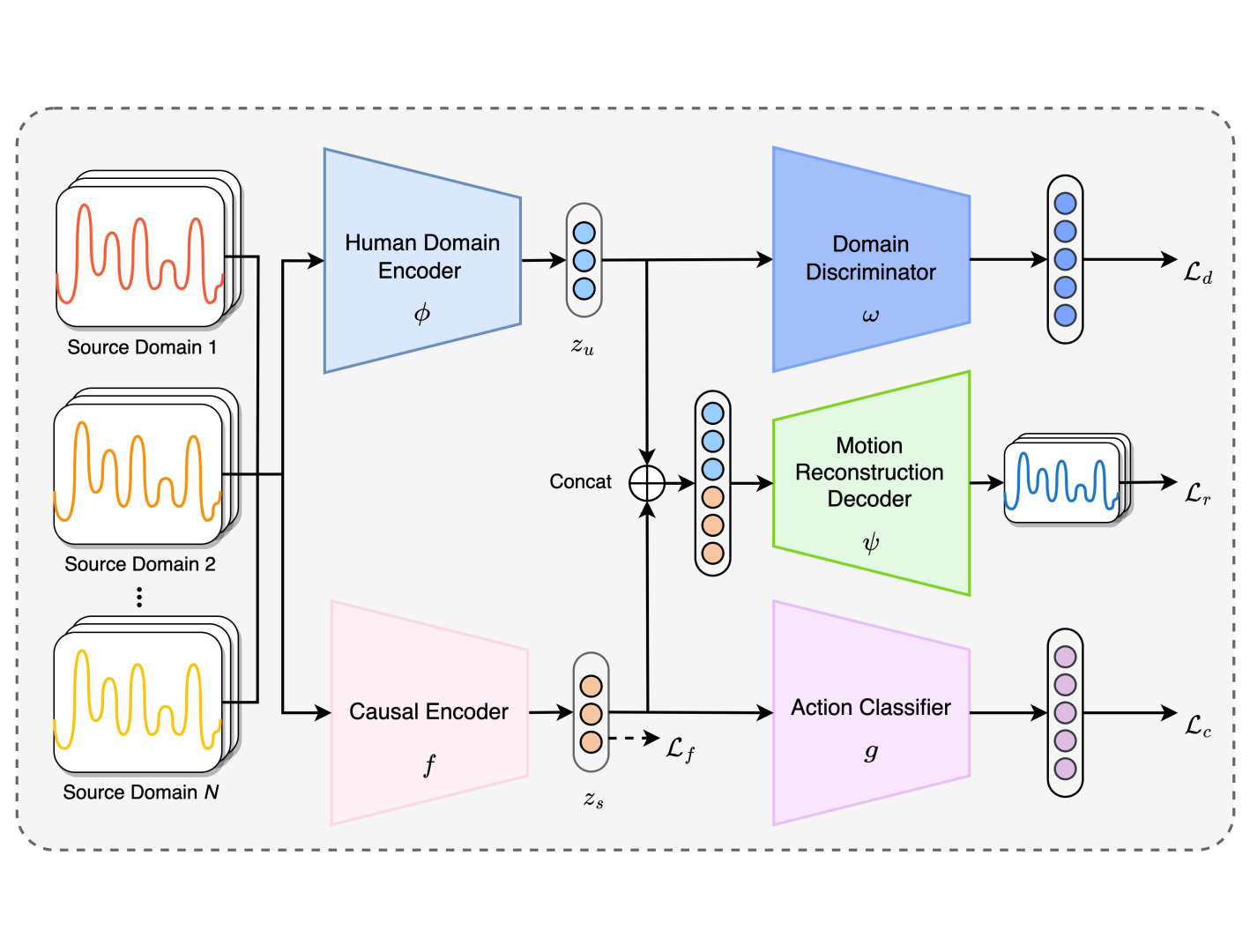 Deep Causal Domain Generalization Network for Human Action Recognition in Internet of BehaviorsRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Bingtao Hu, Zhifeng Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC) , 2024
Deep Causal Domain Generalization Network for Human Action Recognition in Internet of BehaviorsRuirui Zhong, Yixiong Feng, Bingtao Hu, Zhifeng Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC) , 2024The Internet of Behaviors (IoB) aims to leverage advanced sensing and computing technologies to understand human behaviors, and human action recognition is an essential task in IoB. However, recognizing human actions across varied and unseen domains remains a challenging problem, largely due to domain shifts that degrade the performance of conventional models. To address the aforementioned issue, a Deep Causal Domain Generalization Network (DCDGNet) is designed to enhance the generalizability of the human action recognition model. Specifically, a structured causal model for the data generation of human motion is constructed, where human motion signals are decoupled into action class-related causal factors and domain shift-related non-causal factors. DCDGNet integrates a human domain encoder, causal encoder, domain discriminator, motion reconstruction decoder, and action classifier, contributing to the model’s ability to disentangle causal factors from non-causal ones from domain-specific features and achieve domain-invariant representations. Comprehensive experiments confirm that DCDGNet significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of both accuracy and generalizability.
@inproceedings{zhong2024deep, title = {Deep Causal Domain Generalization Network for Human Action Recognition in Internet of Behaviors}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Feng, Yixiong and Hu, Bingtao and Zhang, Zhifeng and Song, Xiuju and Tan, Jianrong}, booktitle = {2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, google_scholar_id = {isC4tDSrTZIC} } - ICNSC 2024
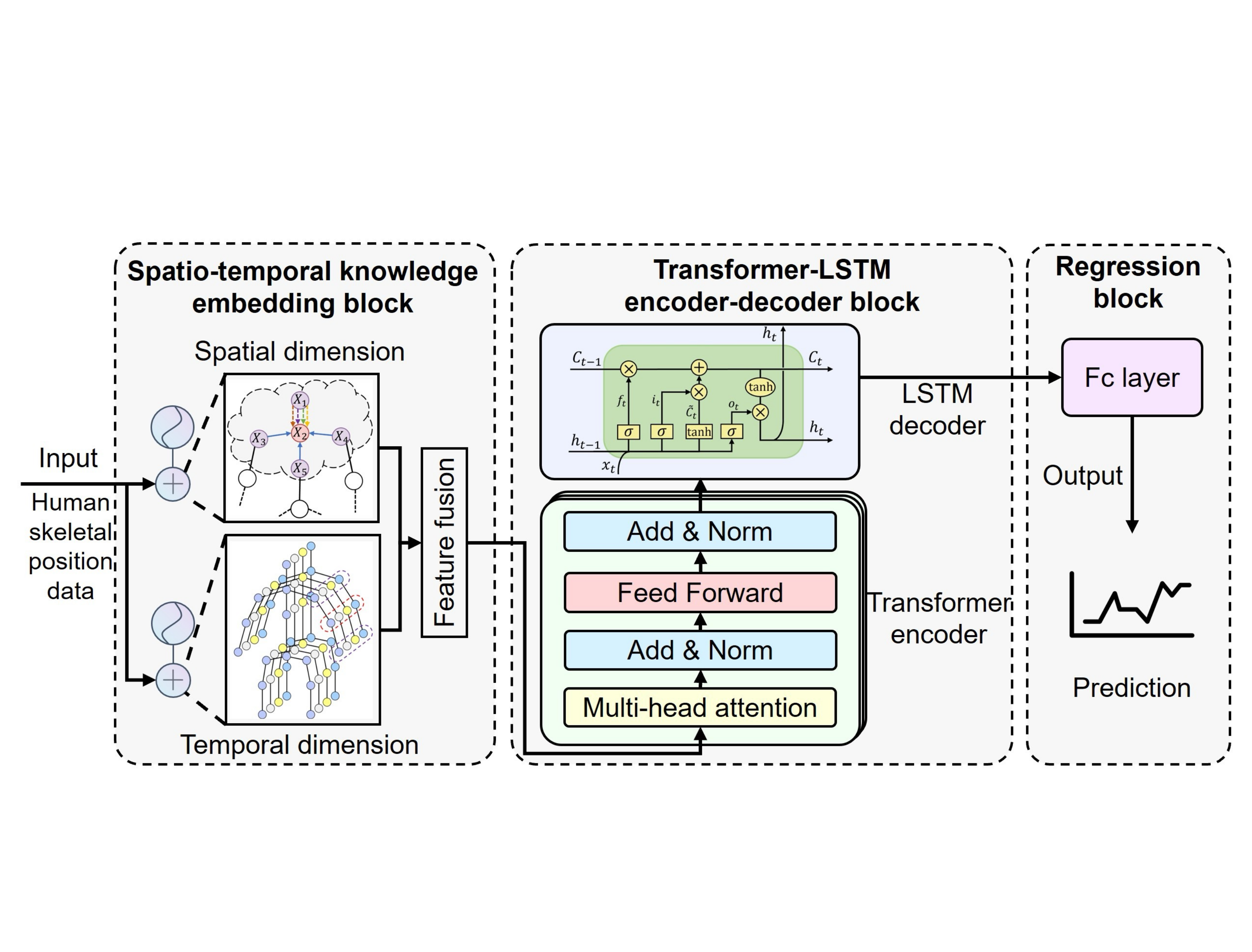 A Spatio-Temporal Transformer Network for Human Motion Prediction in Human-Robot CollaborationYixiu Yuan, Baicun Wang, Ruirui Zhong, and Bingtao HuIn 2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC) , 2024
A Spatio-Temporal Transformer Network for Human Motion Prediction in Human-Robot CollaborationYixiu Yuan, Baicun Wang, Ruirui Zhong, and Bingtao HuIn 2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC) , 2024Efficient human-robot collaboration necessitates bidirectional perception between humans and robots. For robots, understanding the operator’s behavior is crucial for enhancing safety and work efficiency in human-robot collaboration. Human limb movements encompass diverse behavioral information, and accurate human motion prediction has attracted significant attention. Existing human motion prediction methods can extract some behavioral features, but they fall short of fully capturing the dynamic and complex interactions across different time points and body joints in human motion sequences. In this study, a Spatio-Temporal Transformer Network model (STTFN) is proposed to automatically learn the spatio-temporal dependency relationships in human motion sequence data for prediction. The spatio-temporal knowledge embedding block employs an attention mechanism and a graph attention network to extract spatio-temporal behavioral features from raw data. An encoder-decoder network based on Transformer and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) is constructed for further analysis to acquire motion prediction data. This study conducts an experiment utilizing a human-robot collaborative assembly dataset to validate the effectiveness of the proposed model. The results demonstrate that our model outperforms classical models, thereby advancing the field of human motion prediction.
@inproceedings{yuan2024spatio, title = {A Spatio-Temporal Transformer Network for Human Motion Prediction in Human-Robot Collaboration}, author = {Yuan, Yixiu and Wang, Baicun and Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao}, booktitle = {2024 International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, google_scholar_id = {k_IJM867U9cC} } - Neurocomputing
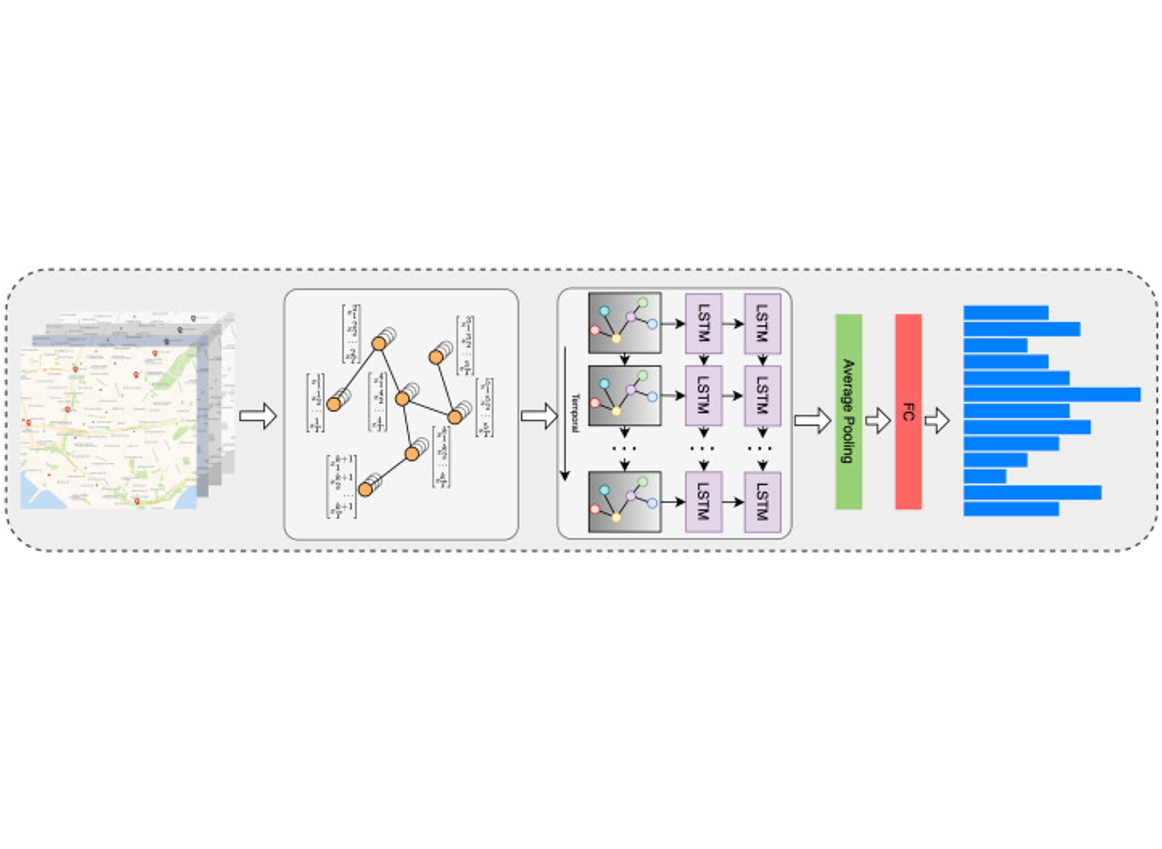 Multi-factor embedding GNN-based traffic flow prediction considering intersection similarityRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Fei Wang, Yixiong Feng, and 5 more authorsNeurocomputing, 2024
Multi-factor embedding GNN-based traffic flow prediction considering intersection similarityRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Fei Wang, Yixiong Feng, and 5 more authorsNeurocomputing, 2024Existing studies on traffic flow prediction primarily rely on on-board devices to collect vehicle trajectory data, which can potentially infringe upon the privacy of users and limit the applicability of the method. Additionally, traffic flow prediction remains challenging due to the complex spatial and temporal dependencies within real-world traffic networks. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a framework for analyzing discrete vehicle trajectory data at urban intersections. By incorporating various external physical factors into traffic flow prediction, this framework derives embedding vectors from vehicle trajectory sequences and road network topology, modeling their spatio-temporal dependencies using Skip-Gram and GraphSAGE, respectively. Additionally, the intersection similarity is introduced to capture and integrate traffic flow patterns between the target intersection and similar intersections. A Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network (ST-GCN) algorithm, which combines Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), is developed to achieve precise traffic flow prediction. Extensive experiments on a real-world traffic flow dataset from Qingdao, China, validate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art baseline methods.
@article{zhong2024multi, title = {Multi-factor embedding GNN-based traffic flow prediction considering intersection similarity}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Wang, Fei and Feng, Yixiong and Li, Zhiwu and Song, Xiuju and Wang, Yong and Lou, Shanhe and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Neurocomputing}, pages = {129193}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Elsevier}, google_scholar_id = {JV2RwH3_ST0C} }
2023
- CJME
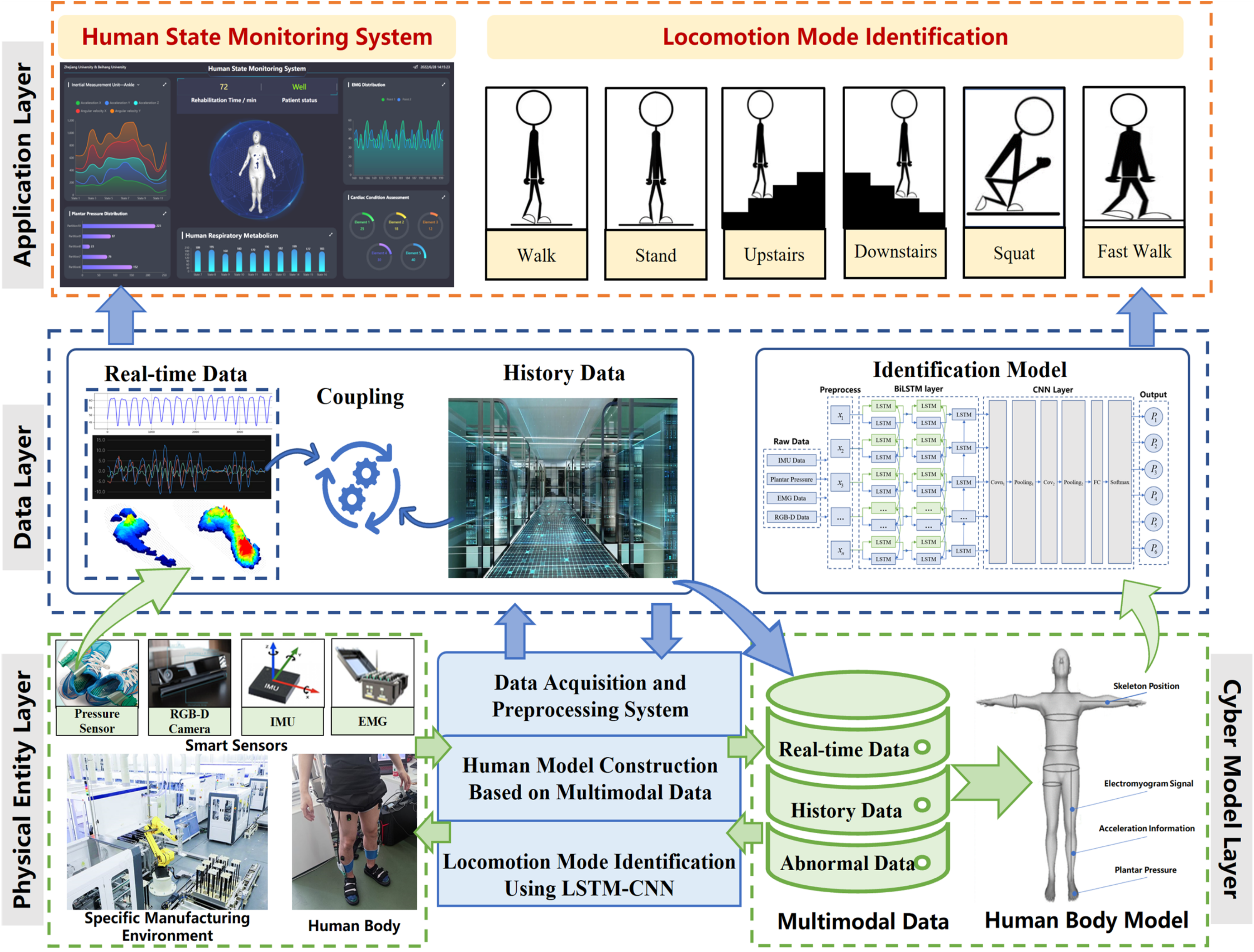 Construction of human digital twin model based on multimodal data and its application in locomotion mode identificationRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Hao Zheng, and 3 more authorsChinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023
Construction of human digital twin model based on multimodal data and its application in locomotion mode identificationRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Yixiong Feng, Hao Zheng, and 3 more authorsChinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023With the increasing attention to the state and role of people in intelligent manufacturing, there is a strong demand for human-cyber-physical systems (HCPS) that focus on human-robot interaction. The existing intelligent manufacturing system cannot satisfy efficient human-robot collaborative work. However, unlike machines equipped with sensors, human characteristic information is difficult to be perceived and digitized instantly. In view of the high complexity and uncertainty of the human body, this paper proposes a framework for building a human digital twin (HDT) model based on multimodal data and expounds on the key technologies. Data acquisition system is built to dynamically acquire and update the body state data and physiological data of the human body and realize the digital expression of multi-source heterogeneous human body information. A bidirectional long short-term memory and convolutional neural network (BiLSTM-CNN) based network is devised to fuse multimodal human data and extract the spatiotemporal features, and the human locomotion mode identification is taken as an application case. A series of optimization experiments are carried out to improve the performance of the proposed BiLSTM-CNN-based network model. The proposed model is compared with traditional locomotion mode identification models. The experimental results proved the superiority of the HDT framework for human locomotion mode identification.
@article{zhong2023construction, title = {Construction of human digital twin model based on multimodal data and its application in locomotion mode identification}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Feng, Yixiong and Zheng, Hao and Hong, Zhaoxi and Lou, Shanhe and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering}, volume = {36}, number = {1}, pages = {126}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer}, google_scholar_id = {d1gkVwhDpl0C} } - CIMS
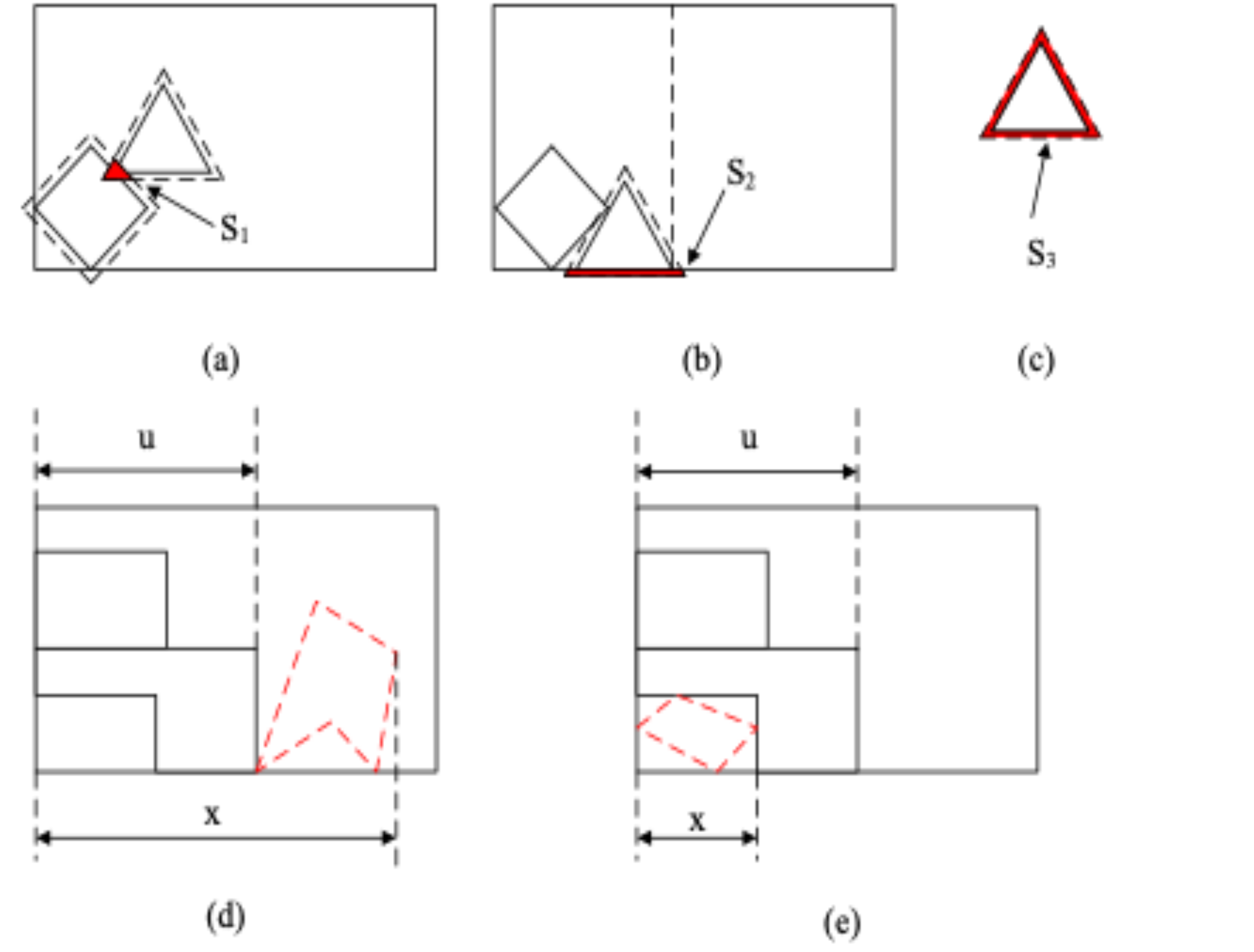 Irregular polygons nesting algorithm driven by design knowledge and applicationYixiong Feng, Ruirui Zhong, Zhifeng Zhang, Cheng Huang, and 4 more authorsComputer Integrated Manufacturing System, 2023
Irregular polygons nesting algorithm driven by design knowledge and applicationYixiong Feng, Ruirui Zhong, Zhifeng Zhang, Cheng Huang, and 4 more authorsComputer Integrated Manufacturing System, 2023To efficiently solve the problem of two-dimensional irregular polygon packing in actual production,a heuristic algorithm driven by design knowledge was proposed.No Fit Polygon (NFP) was used to judge the relative positions between irregular polygons,and a mathematical model of local fitness was established to measure the fitting degree of irregular polygons.Then,a mathematical model driven by design knowledge was established to evaluate the position of irregular polygons to be placed.A greedy algorithm based on local search strategy was used to complete the packing.The experimental testing of international common benchmark cases and comparison with existing intelligent optimization algorithms proved that the proposed algorithm had certain advantages in layout quality and time performance with high stability.Besides,the experimental test of the sample data in actual production proved that the proposed algorithm had the value of being applied to actual production applications.
@article{feng2023irregular, title = {Irregular polygons nesting algorithm driven by design knowledge and application}, author = {Feng, Yixiong and Zhong, Ruirui and Zhang, Zhifeng and Huang, Cheng and Li, Zhongkai and Hu, Bingtao and Hong, Zhaoxi and Tan, Jianrong}, journal = {Computer Integrated Manufacturing System}, volume = {29}, number = {2}, pages = {593}, year = {2023}, google_scholar_id = {hFOr9nPyWt4C} } - ICMD 2023
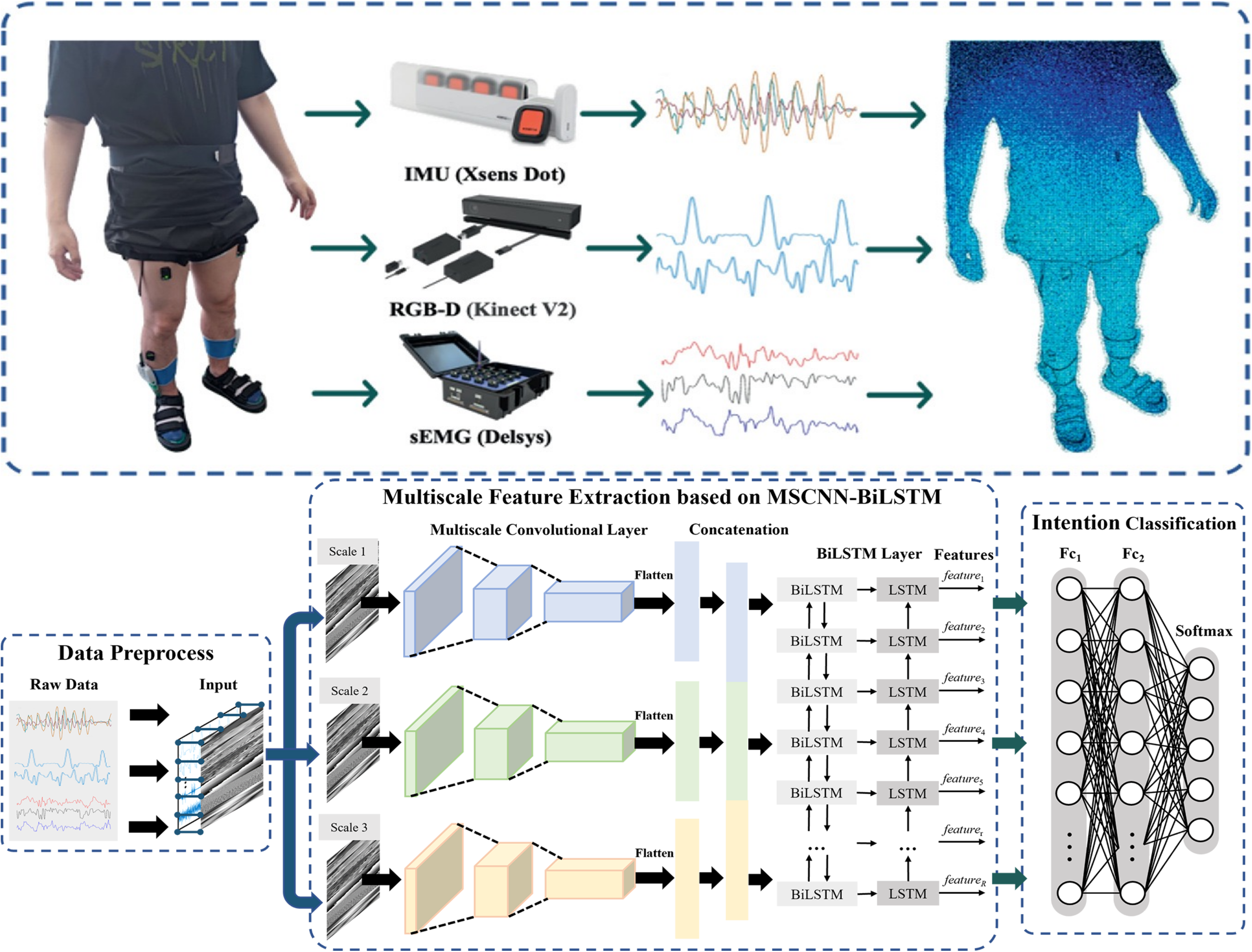 A Human Digital Twin Based Framework for Human–Robot Hand-Over Task Intention RecognitionRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Zhaoxi Hong, Zhifeng Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn ICMD: International Conference on Mechanical Design , 2023
A Human Digital Twin Based Framework for Human–Robot Hand-Over Task Intention RecognitionRuirui Zhong, Bingtao Hu, Zhaoxi Hong, Zhifeng Zhang, and 2 more authorsIn ICMD: International Conference on Mechanical Design , 2023Industry 5.0, the upcoming industrial revolution, places a strong emphasis on human-centric smart manufacturing, redefining the state and role of humans in the process of human–robot collaboration (HRC). The human–robot hand-over task plays a crucial role of HRC, and finding ways to enable robots to understand human handover intentions is an urgent problem to be solved. In this study, a human digital twin-based framework for human–robot hand-over task intention recognition is proposed to enhance the execution efficiency of human–robot hand-over tasks. This framework aims to foster a seamless integration and cooperation between humans and robots, facilitating deep human–robot fusion. Then, considering the multi-scale characteristics and temporal correlation of human intention information, a feature extractor based on multi-scale convolutional neural network and bidirectional long-short-term memory (MSCNN-BiLSTM) is devised to improve the cognitive and collaboration abilities of robots. A series of optimization experiments are conducted to enhance the performance of the MSCNN-BiLSTM model. The superiority of the proposed framework is demonstrated by comparing with traditional human–robot hand-over intention recognition algorithms, which provides an approach to achieve better human–robot fusion and more efficient execution of hand-over tasks.
@inproceedings{zhong2023human, title = {A Human Digital Twin Based Framework for Human--Robot Hand-Over Task Intention Recognition}, author = {Zhong, Ruirui and Hu, Bingtao and Hong, Zhaoxi and Zhang, Zhifeng and Feng, Yixiong and Tan, Jianrong}, booktitle = {ICMD: International Conference on Mechanical Design}, pages = {283--295}, year = {2023}, organization = {Springer}, google_scholar_id = {HDshCWvjkbEC} }





